Reverse Engineering – Strategic Approach for Product Analysis and Innovation
The primary purpose of the method known as Reverse Engineering (RE) is to uncover the complete design and manufacturing history of a product in detail. Beyond analyzing existing products, reverse engineering is used to create new concepts, develop alternative solutions, and design better-performing products that serve the same function with improved efficiency.
This method provides new perspectives on existing products and enables companies to develop high-quality, technologically advanced, cost-effective, and more efficient solutions. As a result, reverse engineering becomes a powerful tool for organizations when establishing roadmaps for new product development.
Reverse Engineering is widely used as a foundation for Product Development, Benchmarking, and Value Engineering studies. In development projects, it serves as the essential groundwork for testing and evaluating existing, competing, equivalent, or similar products.
With the combined expertise of engineering disciplines such as design, construction, development, analysis, and materials engineering, our experienced team provides accurate, high-quality, and fast solutions tailored to our customers’ needs.
Reverse Engineering – Definitions and Context
Reverse Engineering (RE), also known as “Backward Engineering,” originates from the concept of analyzing an existing product to understand how it was built and how it functions.
Common definitions include:
- Dismantling a manufactured product to analyze its components and understand how to reproduce it.
- Studying an existing product, extracting its design principles, and using this knowledge to develop similar or improved versions.
- In software engineering, reverse engineering refers to understanding how a program performs a specific task.
Reverse Engineering involves breaking down a device, object, or system—such as mechanical equipment, electronic components, or software—into its parts and analyzing its structure, function, and operating principles in detail.
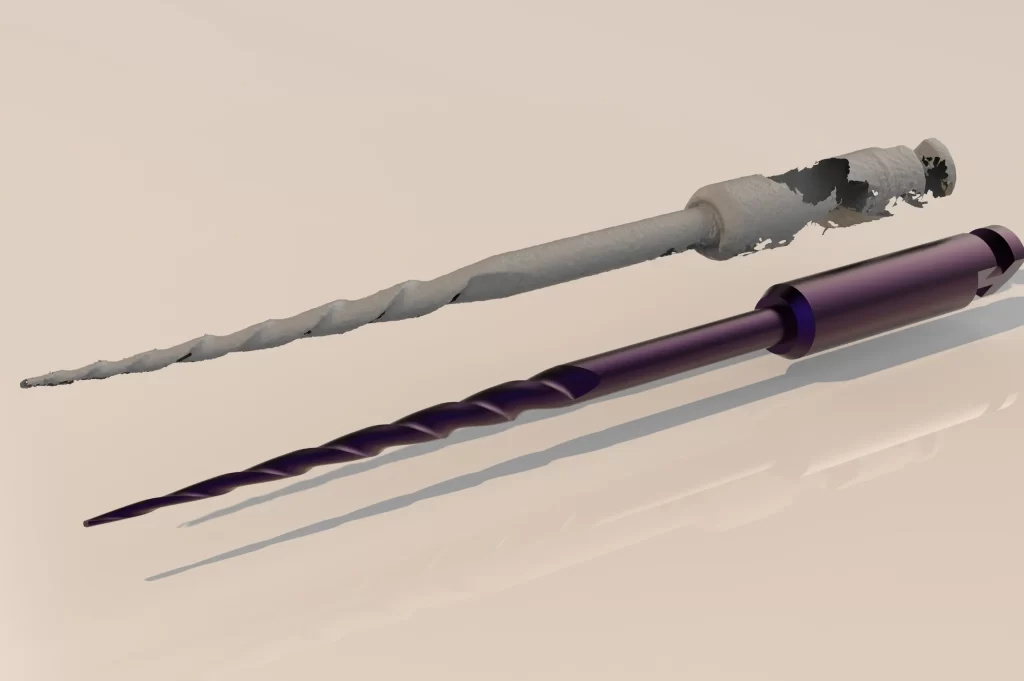


Creating Value Through Analytical and Creative Approaches
To develop a new product or to improve an existing one, it is essential to compare products with similar functions and identify their differences. By applying the widely used SWOT analysis method, companies can determine how to position their new product in the market and identify opportunities for competitive advantage.
SWOT Analysis
- S – Strengths
- W – Weaknesses
- O – Opportunities
- T – Threats
Starting a project with a SWOT-driven approach helps clarify potential improvements, innovations, and competitive features. Regardless of the project type, reverse engineering typically follows a structured top-level plan. This approach involves unveiling product details with a detective-like precision—similar to a “Sherlock Holmes” methodology—turning insights into creative and value-added design improvements.
Through this method, enhanced functionality, lower production costs, and reduced development time can be achieved.
The Strategic Role of Reverse Engineering & 3D Scanning Technologies
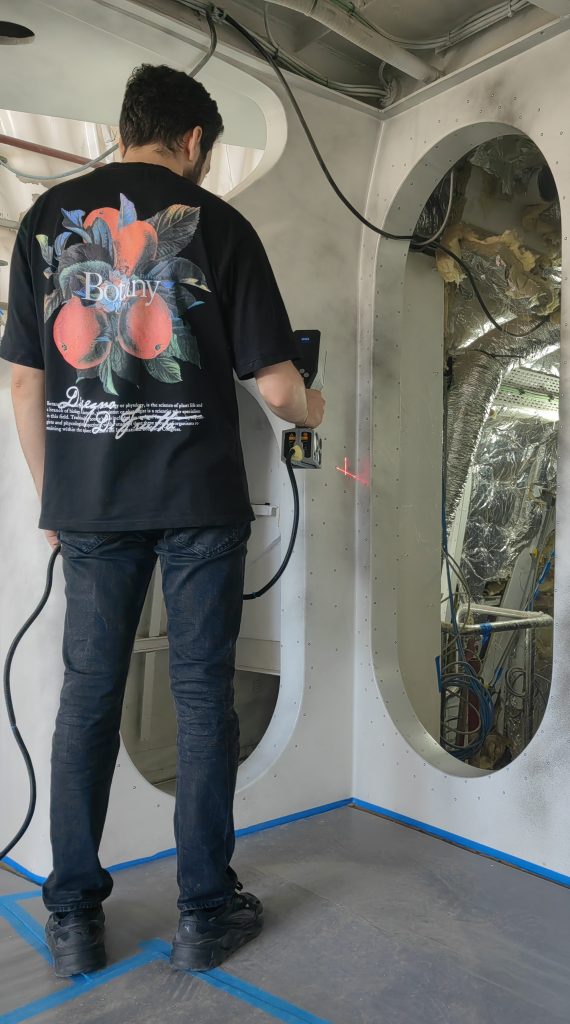
In today’s highly competitive industries, reverse engineering has become a critical tool for optimizing product lifecycle management, accelerating technology adaptation, and enabling innovation. At the core of this approach lie advanced 3D scanning and laser scanning technologies.
Modern 3D scanning systems allow complex geometries to be digitized rapidly, contact-free, and with micron-level precision. This digitalization process forms the foundation of reverse engineering and significantly improves the accuracy of product design and development cycles.
Laser scanning plays a key role in acquiring high-resolution point-cloud data for industrial components. When transferred into CAD environments, these datasets allow engineers to accurately model the geometry of existing products. This reveals manufacturing tolerances, signs of wear, and possible design errors—serving as a powerful decision-support tool in the reverse engineering workflow.
Benchmarking & Competitive Product Analysis
Benchmarking is indispensable for evaluating products against competitors in terms of performance, durability, cost, and manufacturability.
3D scanning and laser scanning enable a detailed and objective comparison of competitor products. When combined with CAD-based reverse engineering models, these findings accelerate the development of new product concepts and strengthen engineering decisions.
Innovation-Driven Product Improvement
3D scanning is used not only for replicating existing products but also for supporting innovation and improvement processes. Engineering and R&D teams rely on highly accurate scan data to develop superior designs in terms of ergonomics, structural integrity, and aesthetics. This shortens development cycles and reduces costs.
Sectors such as defense, automotive, white goods, medical devices, and mold-making have already adopted 3D scanning–supported reverse engineering as an integral part of their quality assurance systems.
Laser scanning also plays a critical role in root-cause analysis for production errors. By comparing a manufactured part with its ideal CAD model, deviations can be identified at a micron level. This provides essential insights for design and manufacturing improvements and strengthens the overall product development workflow.

Conclusion
3D scanning, laser scanning, reverse engineering, product design, product development, and benchmarking together form an inseparable ecosystem in today’s industrial competition landscape. Integrating these technologies enables the creation of high-precision, fast, cost-effective, and innovative products.
With this approach, our company delivers comprehensive DESIGN – DEVELOPMENT – ENGINEERING and sustainable product solutions for industrial clients.
